This blog provides an overview of heliport and helideck lighting systems, with a focus on the operational and regulatory implications of ICAO Annex 14 Volume II, CAP 437, and ATEX requirements. It is written for industry professionals with a background in aviation or offshore operations who need clear insights into compliance, build quality, and technical functionality.
Lighting as an operational safety system
In helicopter operations, visual landing aids (VLAs) are critical. Proper lighting enables pilots to maintain spatial orientation, especially during fog, night-time operations, or heavy marine conditions. A well-integrated lighting layout enhances safety margins while also supporting standardised decision-making during approach and landing.
Lighting also serves a compliance function. International standards allow operators to create environments where pilots can quickly recognise landing zones, regardless of weather or regional variations in infrastructure.
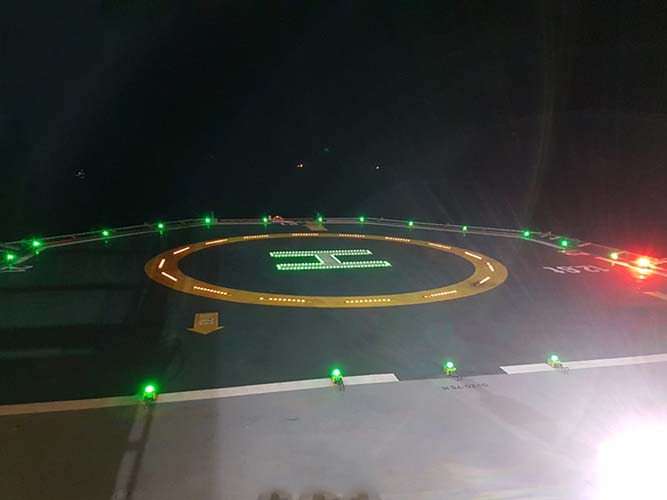

Standards-driven design: ICAO Annex 14 vs CAP 437
ICAO Annex 14, Volume II
Annex 14 Vol. II is the global reference for heliport and helideck design, including all lighting aspects. It outlines:
- Light spacing and intensity for FATO and TLOF zones
- Colour conventions (white for FATO, green for TLOF)
- Maximum fixture heights
- Uniform beam angles
- Preferences for inset vs surface-mounted fittings
Though not legally binding, ICAO’s guidelines are widely used by civil aviation regulators and are particularly suitable for non-oil offshore applications, such as wind farms, survey vessels, and hospital helipads.
CAP 437
For operators in the UK Continental Shelf, Norwegian waters, or other North Sea jurisdictions, CAP 437 is the recognised standard. Published by the UK Civil Aviation Authority, it mandates:
- Use of ATEX-certified explosion-proof lighting
- TD/PM Circle and “H” lighting with defined intensities
- Green perimeter lighting (with floodlights discouraged)
- Low-profile fittings (≤25 cm, ideally ≤15 cm)
- Strict beam angle testing and documentation
While CAP 437 is primarily for the offshore oil and gas industry, its principles are increasingly applied to other sectors.
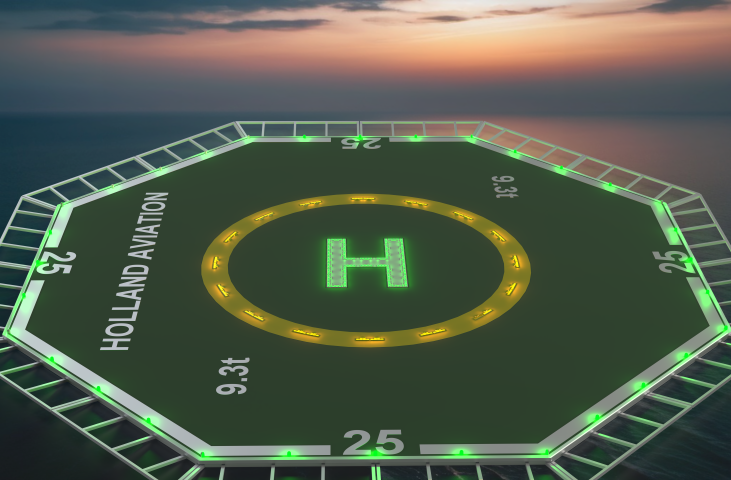
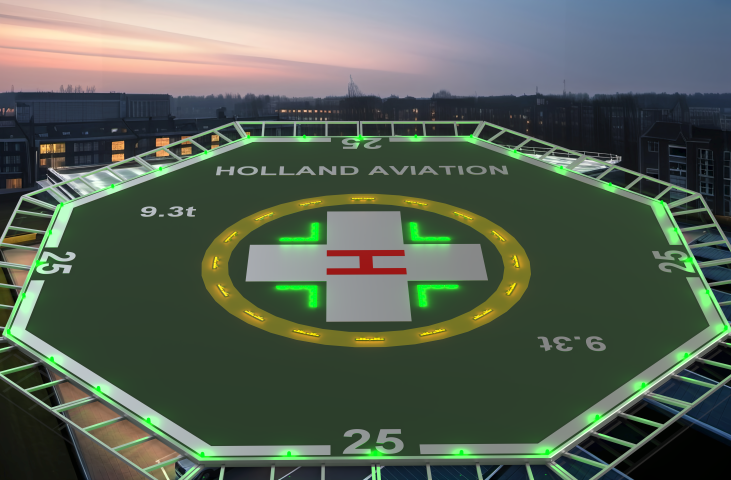


Evolution of helideck lighting requirements
Historically, earlier editions of ICAO and CAP 437 were less strict. Key updates over the years have included:
- Removal of orange lighting due to its tendency to attract birds
- Phasing out of floodlighting to prevent “black hole” illusions on approach
- Mandatory use of TD/PM Circle and “H” layouts for landing alignment
These changes are based on accident reports and pilot feedback, helping to make landings safer, especially offshore or in poor visibility.
ICAO now includes offshore guidelines, which means CAP 437 is no longer needed in low-risk areas where ATEX or full offshore systems aren’t required.
Cost Pressures and over-compliance
Many operators in offshore wind, maritime research, and hybrid-use vessels face challenges related to over-compliance. CAP 437’s ATEX requirement, while justified in oil and gas, can drive up costs and maintenance complexity in non-hazardous environments.
For example, wind farm vessels, cable layers, and superyachts often install full ATEX systems, despite operating in Zone 2 or non-hazardous areas. Several flag states now accept non-ATEX-rated lighting behind the ship bridge or in protected locations. LNG carriers are a prime example, where exemptions have been granted based on risk assessments.
Holland Aviation offers ICAO-compliant systems tailored to these needs, delivering regulatory alignment without unnecessary cost.
System components: a technical summary
FATO Lighting
White omnidirectional fittings spaced up to 50 metres apart on square pads or 10 metres on circular ones. Beam intensity is capped at 100 candela between 3–20° vertical angle.
TLOF Lighting
Green perimeter lights mark the touchdown area. ICAO allows heights up to 25 cm. ( CAP 437 restricts this to 15 cm.) For elevated decks, inset fixtures (≤2.5 cm height) are used at 3 m intervals.
TD/PM Circle and “H” Lighting
Defines the touchdown geometry with at least 16 illuminated segments. Light output ranges from maximum 30–60 candela for the circle and graded intensity for the “H” character.
Floodlighting
Used after landing for passenger disembarkation. Offshore installations typically use HA–OSFX floodlights. Onshore helipads use HeliFLO models.
Status Lighting
Red warning lights indicate when a deck is unsafe for operations. These integrate with helideck monitoring systems (HMS).
Heliport Beacons
Rotating or flashing Morse “H” beacons with a minimum intensity of 2,500 candela. Used for long-range identification in high-background environments.
Approach Path Indicators
Options include HAPI, CHAPI ,and APAPI systems. These provide glide slope reference with red, green, and white cues. CHAPI uses a narrow green window for precision landings.
Windsocks
Internally lit, UV-resistant and mounted on 316 stainless steel masts. ICAO and CAP 437 require clear visibility from the main approach, both day and night.
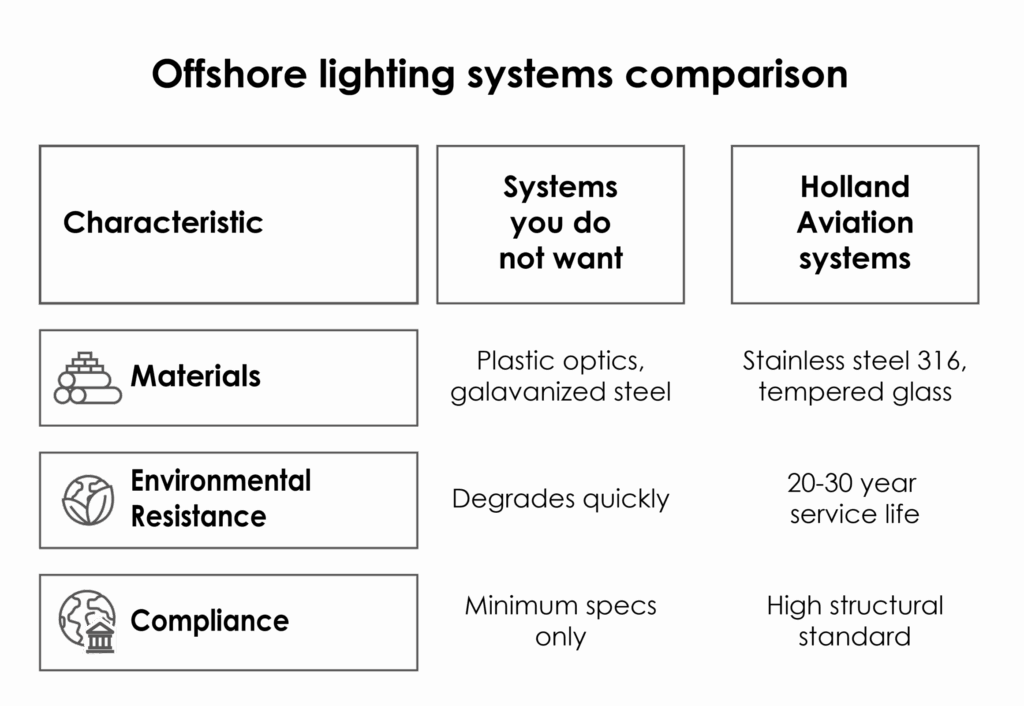
Materials, durability, and lifecycle considerations
Offshore lighting systems are exposed to extreme UV radiation, wind, salt spray, and vibration. Some manufacturers use plastic optics or galvanized steel, which initially meet minimum specs but degrade quickly. Plastics tend to yellow or crack, and galvanised parts corrode in marine air.
Holland Aviation uses stainless steel 316 for offshore installations and tempered glass optics for maximum clarity and lifespan. Our systems are engineered for a 20 to 30-year service life in harsh maritime conditions.
Where ATEX compliance is not required, we supply non-atex versions built to the same structural standard, providing durability without overcapitalisation.
Certifications and global project experience
Holland Aviation systems are manufactured under:
- ISO 9001 (Quality Management)
- ISO 14001 (Environmental Responsibility)
- ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety)
- ICAO-compliant lighting with optional third-party certification
Innovation for a changing industry
We continue to invest in next-generation lighting systems. Our development roadmap includes:
- NVG-compatible fixtures
- Solar-integrated designs
- Remote diagnostics and monitoring
- Smart dimming and ambient-response lighting
- Flexible kits for ICAO and CAP 437 hybrid applications
As ICAO and CAP 437 evolve, we ensure that our systems remain compliant, future-ready, and adaptable across a wide range of operating environments.
Contact us
Need a project-specific quote, technical documentation, or support with compliance?
Holland Aviation – Trusted by aviation professionals since 1968. Compliant. Reliable. Built to last.
